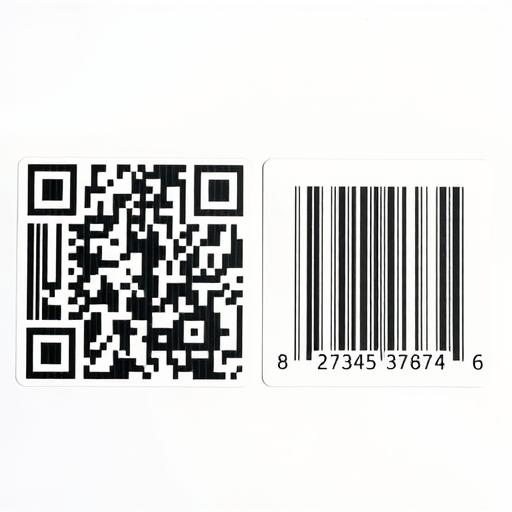
In a world increasingly driven by technology, both QR codes and barcodes play essential roles in various industries, streamlining processes and enhancing access to information. Despite both being used for data storage and retrieval, they differ in technology and application. Understanding these differences can help businesses and consumers choose the most effective option for their needs.
Contents
- What are Barcodes?
- What are QR Codes?
- Key Differences Between QR Codes and Barcodes
- Common Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs – QR Codes & Bar Codes
What are Barcodes?
Barcodes are graphical representations of data that can be read by optical scanners. They typically consist of a series of parallel lines with varying widths and spaces, encoding data in a one-dimensional format. The most common types of barcodes include UPC (Universal Product Code) and EAN (European Article Number). Barcodes primarily store limited information, such as product identification numbers and prices.
What are QR Codes?
QR codes (Quick Response codes) are two-dimensional codes that can store significantly more information than traditional barcodes. Shaped like a square grid, they consist of black squares arranged on a white background. QR codes can store URLs, text, contact information, and more. They were originally developed for tracking automotive parts but have since expanded to various industries due to their flexibility and ease of use.
Key Differences Between QR Codes and Barcodes
- Data Capacity: Barcodes can typically store 20-25 characters, while QR codes can hold more than 4,000 characters. This makes QR codes more suitable for applications involving larger data sets.
- Scanning Technology: Barcodes require a laser scanner or dedicated barcode reader to interpret their data, while QR codes can be scanned using a smartphone camera or any optical device capable of reading images.
- Usability: QR codes can be scanned from any angle, making them easier to use in dynamic environments. Barcodes must be aligned correctly for successful scanning.
- Symbology: Barcodes are linear (one-dimensional), while QR codes are matrix (two-dimensional), housing data in both vertical and horizontal orientations.
Common Applications
Barcodes and QR codes are utilized across numerous sectors, including:
- Retail: Barcodes are prevalent in point-of-sale systems for inventory management and pricing. QR codes are increasingly used for marketing, promotions, and customer engagement.
- Logistics: Barcodes are essential for tracking packages and shipments. QR codes can provide instant access to product information, tracking updates, or supply chain data.
- Healthcare: Barcodes are used for patient identification and medication management. QR codes can help healthcare providers share information quickly, such as lab results.
- Education: Barcodes are often used for book checkouts in libraries, while QR codes can provide access to supplemental materials, lectures, and interactive media.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between QR codes and barcodes is essential for businesses and consumers alike. While both technologies serve the purpose of data storage and retrieval, they achieve it in fundamentally different ways suited to different applications. By leveraging these technologies properly, organizations can enhance efficiency and improve the customer experience, seamlessly integrating these tools into their operational strategies.
FAQs – Qr Codes & Bar Codes
Q: Can I create my own QR codes?
A: Yes, numerous online tools and software applications allow users to generate QR codes for free or at a nominal cost. You can customize them with logos or colors while retaining functionality.
Q: Are QR codes secure?
A: QR codes themselves do not hold sensitive data. However, they can point to websites that may contain personal information. It’s advisable to be cautious when scanning QR codes from unknown sources.
Q: Can barcodes be scanned using a smartphone?
A: Standard one-dimensional barcodes require a dedicated scanner for optimal reading. However, many smartphones now come with apps capable of scanning barcode formats.
Q: Do QR codes need an internet connection to function?
A: QR codes can link to offline content, but if the code directs users to a website, an internet connection is necessary to access it.
Where can I get a Qr Code generated?
Need a Qr Code which you can capture user data with and re-direct users to different parts of your website depending on their location? GeoQrCodes has you covered. Start generating your Geo-enabled Qr code free with us today at GeoQrCodes.com!